Recognized in

®

™ Voice of the Customer 2025 for Brand Protection and External Attack Surface Management


Prevent BEC & Email Attacks with Proactive Phishing Intelligence
Prevent BEC & Email Attacks with Proactive Phishing Intelligence
Email phishing attacks and social engineering are among the most common cybercrimes across the world. However, in recent years, phishing scams have evolved from spammy emails to sophisticated, targeted campaigns.
Read Time
7 min read
Posted On
May 16, 2025
Social Media
Email phishing attacks and social engineering are among the most common cybercrimes across the world. However, in recent years, phishing scams have evolved from spammy emails to sophisticated, targeted campaigns. Such highly personalized scamming trends impersonate trusted brands or notable executives, exploit behavioral psychology, and bypass legacy security systems using modern technology. The use of duplicated creatives, brand voice, logos, and other trust symbols makes it quite difficult to distinguish the fakes from the real brand materials, even for the most attentive and tech-savvy people. Additionally, the use of AI technology to mimic a brand’s signatures can enhance the visual accuracy catastrophically, making it difficult to identify the difference without sophisticated phishing detection techniques.
In 2025, when most organizations rely on email sign-ups for lead generation and marketing purposes, email phishing attacks will become one of the leading causes of data breaches, ransomware infections, and financial fraud. With AI-powered phishing intelligence, deepfake voice messages, and real-time domain spoofing, cybercriminals are scaling their attacks faster than ever. Thus, it is imperative for businesses to install effective phishing detection techniques to identify and prevent phishing scams from stealing sensitive organizational data or executing malware attacks.
What Are Phishing Email Attacks?
Phishing means a form of social engineering attack where attackers impersonate legitimate entities, such as banks, SaaS platforms, or trusted executives, to trick recipients into revealing sensitive data, downloading malware, or executing financial transactions. Delivered primarily via email or text messages, phishing scams are often the first step in more complex cyberattacks.
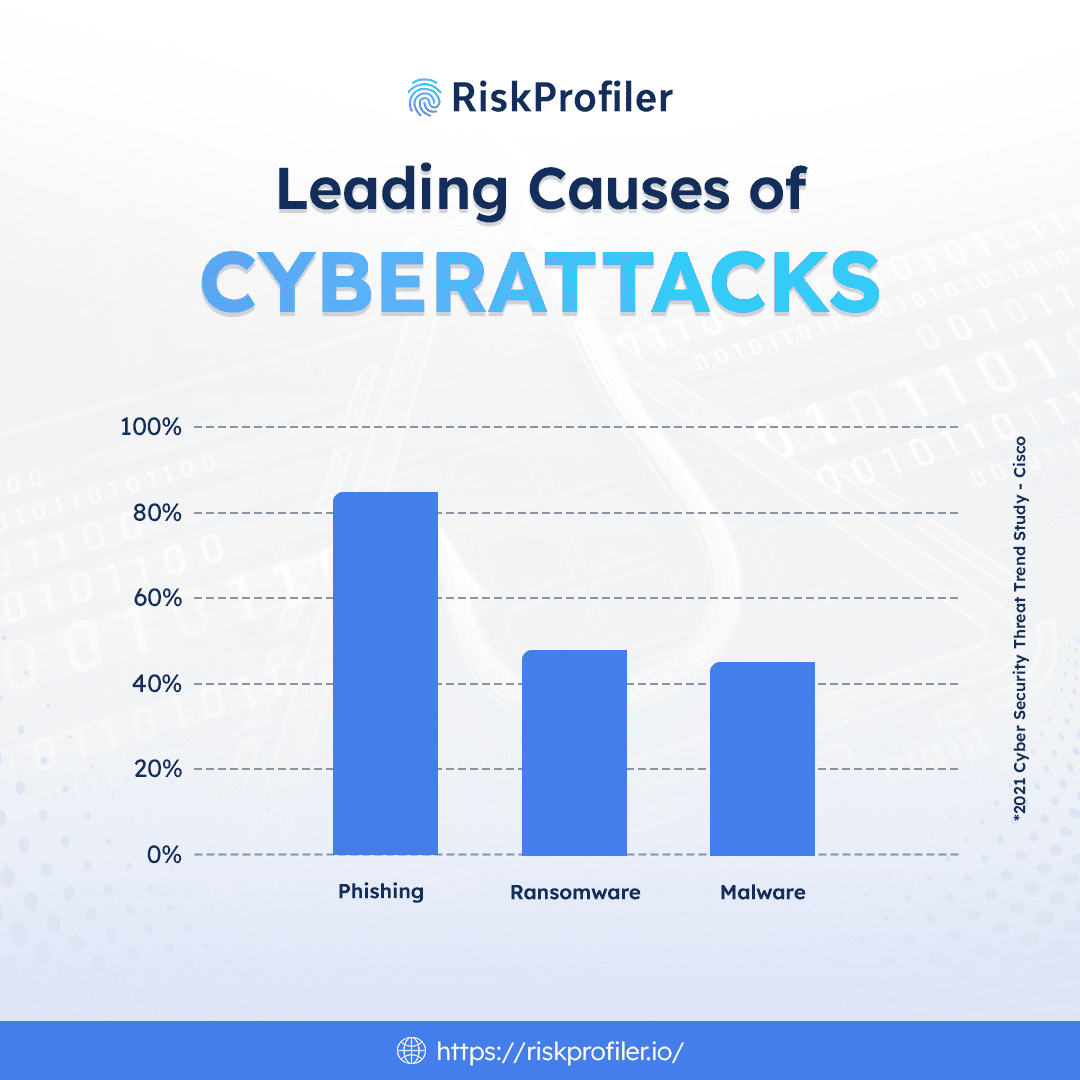
According to the 2021 Cyber Security Threat Trends study conducted by Cisco, 86% of organizations encountered a phishing attack, while the ransomware and malware attack attempts are at 50% and 48%, respectively. A majority of these phishing scams are directly linked to ransomware launches, taking down operations, causing data leaks, financial losses, and considerable damage to organizational trust and reputation.
So, how do employees fall prey to such social engineering attacks? The answer is simple, with careful manipulation.
The content of email phishing attacks uses manipulative language, preying on the receiver’s urgency, trust, and fear in various degrees. Attackers can also imitate trusted executives, advisors, or employees to gain access to sensitive PII details, accelerate app permissions, and complete financial transactions. In the absence of proper phishing detection techniques, organizations can easily fall victim to such fraudulent practices.
Different Types of Phishing Email Attacks
Scammers and cyber attackers use diverse, deceiving methodologies to execute email phishing attacks. With modern cyber threat techniques, criminals now deploy unique phishing plans, each tailored to specific victim identities, platforms, and attack goals using modern technical innovations or AI-assistance. Recognizing these email attack types and their intent is critical for building a robust defense strategy and educating employees on how each variant operates.
In this section, we will be discussing the most common phishing attacks, their targets, and attack intent in detail.
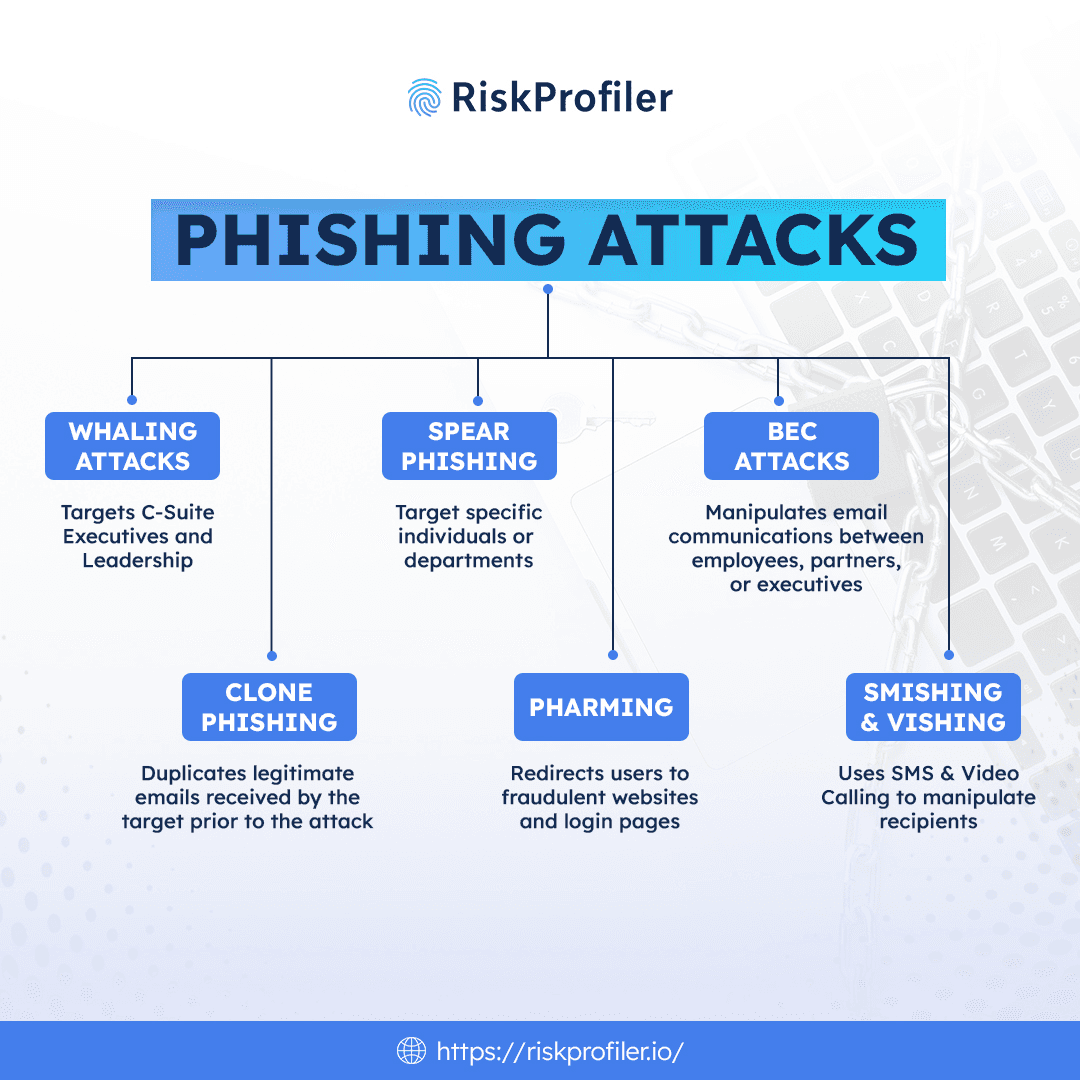
Spear Phishing Attacks
Cyber attackers use Spear Phishing tactics to target specific individuals or departments using personalized information gathered from public sources or prior breaches. These emails often reference internal systems, colleagues, or current projects to build credibility. Thus, these malicious entities often utilize previously stolen information like PII details or sensitive business data from dark web data dumps to carry out attacks on their targets and establish a sense of trust. Since the messages feel relevant and familiar, recipients are more likely to click on malicious links or share credentials, making spear phishing one of the most dangerous forms of email-based attacks.
Whaling Attacks
Whaling attack is a spear phishing campaign where cybercriminals focus specifically on high-level executives such as CEOs, CFOs, or board members. These attacks typically use high-stakes scenarios, like legal threats or urgent financial decisions, to manipulate their targets into seeking immediate action. Because executives often have greater access privileges and weaker scrutiny on their communications, whaling attacks can lead to significant financial losses or reputational damage.
Clone Phishing Attacks
Attackers can, at times, duplicate a legitimate email or text previously received by the target from a trusted contact or known vendor in an attempt to gain the receiver’s trust and influence them to take action. The cloned versions of such emails include identical formatting but swap out the original attachment or link with a malicious one. Victims are easily tricked since the message appears familiar and trustworthy, making this a stealthy and highly effective technique.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC or cyber attacks using Business Email Compromise manipulate email communications between employees, partners, or executives to execute unauthorized actions, such as wire transfers or sensitive data sharing. Attackers may compromise real accounts or create lookalike domains to impersonate internal personnel. BEC attacks are often devoid of malware, making them harder to detect using traditional security filters and requiring behavioral analysis for identification.
Pharming Attacks
Pharming redirects users to fraudulent websites and login pages, even when the correct URL is entered, by exploiting DNS vulnerabilities or infecting a user’s device. These fake sites often mimic login pages of financial institutions, email providers, CRM tools, or internal portals to steal credentials. Unlike phishing emails, pharming doesn’t always require direct user interaction, making it particularly insidious and hard to detect.
Smishing & Vishing Attacks
Smishing (SMS phishing) and vishing (voice phishing) extend phishing tactics beyond email. In smishing, attackers use text messages to deliver malicious links or request sensitive information. Vishing involves fraudulent phone calls, often impersonating customer support or financial institutions. These tactics exploit urgency and trust, and are commonly used in multi-channel phishing campaigns targeting mobile users or remote employees.
Why Is Phishing Detection Using Machine Learning & AI Critical in 2025?
Traditional email security methods such as static blacklists, rule-based filtering, and signature matching were once effective against basic spam and malware. But in 2025, when phishing attacks have become polymorphic, highly targeted, and increasingly evasive, the legacy phishing and manipulation detection systems will not be as useful in detecting particularly advanced phishing emails. Attackers now use advanced tools and AI technologies to craft realistic language, spoof sender identities, and even mimic organizational identity and behavior.
Thus, enabling phishing detection using machine learning can analyze communication patterns, interpret email context, and identify threat signals that humans or legacy tools would miss. Implementation of AI threat detection is not only for risk identification. These advanced modules learns to recognize user behavior and familiar patterns in real-time and adapt with them, to quickly flag anomalies with the most subtle deviation from their usual paths.
Contextual Awareness
AI Large Language Models are trained on billions of messages and are capable of recognizing behavioral patterns from text. Thus, these models are capable of not only interpreting the content but also the intent behind an email. They assess tone, urgency, sentence structure, and historical communication patterns for a detailed contextual analysis. On detection of any suspicious or unusual activity, the system flags it and shuts down the communication.
For example, if an employee suddenly receives an email from a “CEO” demanding an urgent wire transfer, AI can flag the anomaly even if the language appears polished and error-free.
Protection from Zero-Day Phishing Attacks
Zero-day phishing threats are a type of phishing risk where attackers exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems without any prior knowledge. Often in cases of zero-day phishing attacks, attackers target a large number of individuals from the same company to execute their campaign. These scamming techniques can, at times, bypass static filters because they use novel domains, fresh language, and unlisted URLs.
Although these kinds of targeted campaigns can be missed during manual checks, AI modules identify the attack strains easily. AI doesn’t rely on previously known indicators of compromise to recognize a pattern. Instead, it evaluates the behavior, structure, and metadata of each message in real time, flagging suspicious activity even if it’s the first of its kind.
Adaptive Learning
AI systems are trained to learn from new data and evolve with it continuously. As phishing campaigns continue to grow in numbers and diverse attack techniques, the model’s understanding of these tactics keeps evolving with it. This adaptability allows for the detection of newly emerged phishing strains, especially those using advanced obfuscation techniques, visual deception, or multi-stage payload delivery. With AI growing to recognize the attack patterns, the detection and neutralization process grows more favorable for the security teams.
Anomaly Detection with Behavioral Analytics
Enhancing phishing detection using machine learning and AI modules can build a behavioral baseline for each user. This is built based on communication patterns, email sending hours, typical time zones, who they interact with, and their IP signatures. When the machine detects any deviation from this norm, such as an unexpected login location or off-hour message requesting financial action, the system generates high-fidelity alerts without manual input.
Real-Time Decision Making
Speed is of utmost importance when it comes to phishing defense. AI-powered threat detection systems can analyze and score an email’s risk within milliseconds. Followed by this detection, the modules instantly quarantine or flag the dangerous content, blocking all forms of interactions with the contents of the malicious phishing emails. This prevents the user from even viewing the phishing message, reducing response time and minimizing risk exposure.
Streamlined Threat Response
AI-ML modules do not stop at simply detecting phishing threats, they also enable faster, more efficient responses. Once a phishing email is flagged, AI-driven systems can automatically quarantine the message, notify affected users, update threat intelligence feeds, and trigger predefined incident response workflows. This automation dramatically reduces response times and eliminates the bottlenecks of manual triage, allowing security teams to focus on strategic remediation rather than routine firefighting.
Real-World Examples of Phishing Email Attacks
Understanding phishing attacks on companies and their real-world consequences helps illustrate just how conniving and damaging these social engineering attacks can be. Below are some notable phishing attack examples from recent years that highlight evolving attacker tactics and the real consequences of failing to detect them.
Microsoft 365 BEC Campaign (2024)
In 2024, a massive Business Email Compromise (BEC) campaign exploited lookalike domains and impersonated Microsoft 365 support. The attackers sent highly convincing fake invoice emails to finance departments and key personnel across the globe using spear-phishing and adversary-in-the-middle procedures (AiTM). By mimicking internal workflows and targeting shared inboxes, they successfully harvested credentials from over 10,000 companies. Once inside, they initiated unauthorized payments and exfiltrated sensitive financial data, causing millions in aggregate losses.
Crypto Exchange Executive Deepfake (2022)
One of the most startling phishing attacks involved a deepfake video call used to impersonate Binance, the reputed cryptocurrency exchange’s Chief Strategy Officer, Patrick Hillmann. The attackers, using AI-generated visuals and voice synthesis, convinced several crypto community members to interact with the entities regarding asset listing on the crypto exchange platform. The video appeared so realistic that no red flags were raised during the conversation. This incident marked a chilling shift in phishing tactics, where real-time AI impersonation replaced traditional fake emails and documents.
Healthcare Ransomware Phishing Attack (2020)
A phishing campaign disguised as a series of urgent COVID-19 policy updates infiltrated several major US hospitals. The spear phishing emails originated from one of the business executives of Haier Biomedical. In another incident, NCSC detected phishing incidents deploying the “Agent Tesla” malware into a hospital system by disguising itself as Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the Director-General of WHO. Entire hospital systems faced outages, with patient records, lab scheduling, and billing operations affected. Emergency response teams were forced to revert to manual processes, causing dangerous delays in patient care and costing millions in recovery efforts.
Gamma Platform Exploited for Microsoft Credential Theft
Cybercriminals abused the newly launched AI-powered Gamma presentation platform to host phishing pages mimicking Microsoft SharePoint logins, leading to unauthorized access to corporate accounts. In this phishing campaign, attackers use previously compromised email accounts to share phishing emails with users, requesting them to open the embedded PDF document. Opening this PDF leads to a phishing site mimicking Microsoft’s login page with CAPTCHA verification, establishing a false sense of trust with the interacting user.
Top 10 AI Phishing Detection Techniques in 2025
Phishing intelligence is a crucial component of the security protocols in today’s date, given the steep rise in phishing scams. The modern phishing scams are advanced with diligent obscuring techniques, which require AI phishing detection techniques integration for fast identification and takedown. Some of the phishing detection techniques that help you secure your organization and employees from impersonation are listed below.
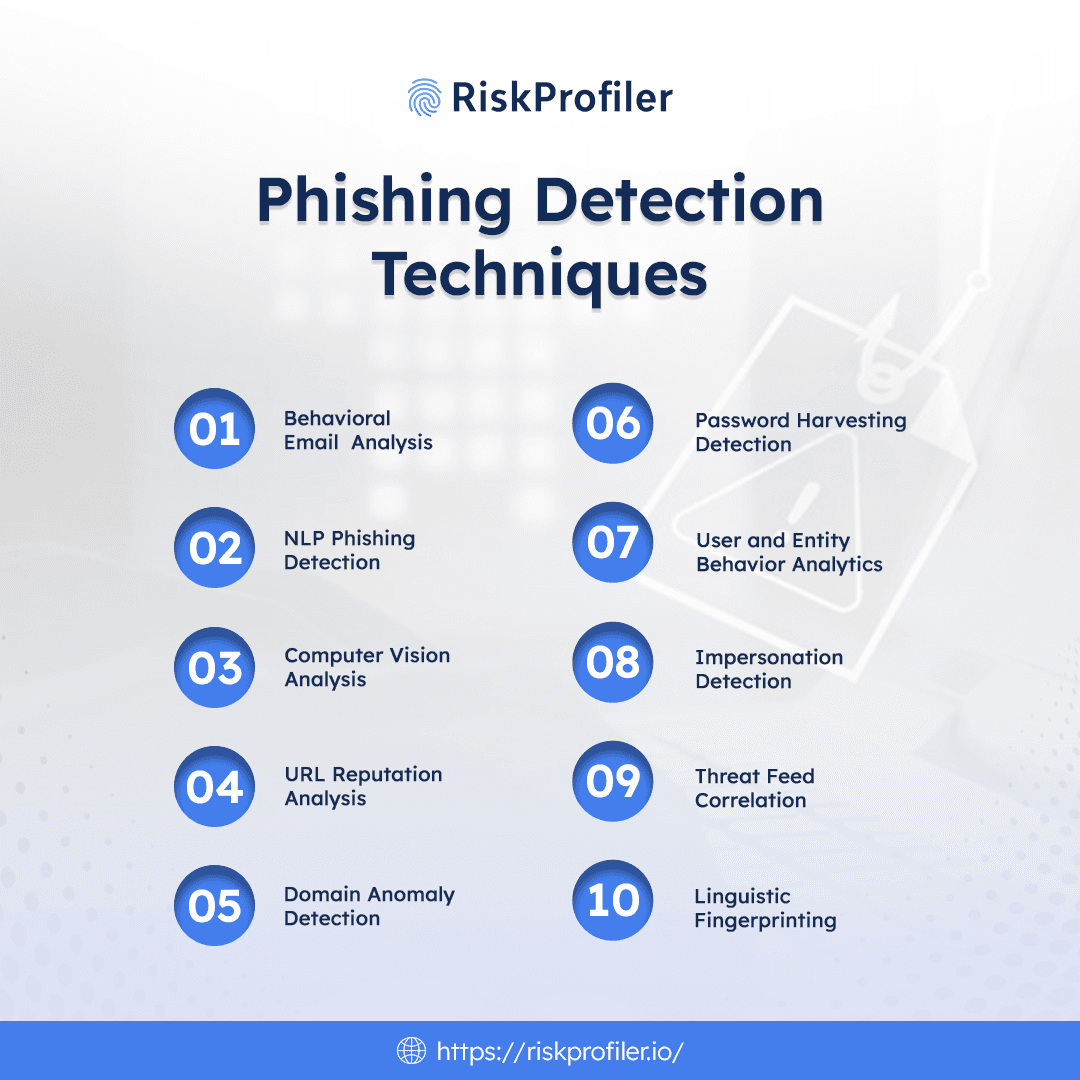
Behavioral Email Analysis
Behavioral analysis for email threats is one of the most effective phishing detection techniques, where AI modules monitor patterns in sender behavior. The key components of such email security solutions and related analysis include tracking important metadata such as IP addresses, login geographies, and sending times to flag anomalies. The detected and analyzed data is then compared to common business patterns related to trusted senders to flag anomalies.
For example, if a trusted vendor who normally sends invoices from a U.S.-based server suddenly sends an email at 3:00 AM from an Eastern European IP, the system flags it for immediate review. This technique excels at detecting insider threats and compromised accounts.
Natural Language Processing or NLP Phishing Detection
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables email security tools to read and interpret the tone, sentiment, and linguistic structure of messages. Phishing emails often use manipulative language such as urgency, fear, or pressure tactics to influence recipients into taking faster actions.
NLP phishing detection modules evaluate these cues and cross-reference them against known phishing patterns. More advanced models also detect contextual oddities. Such patterns include a supplier suddenly requesting login credentials or an unfamiliar tone from a colleague. This allows for near real-time threat scoring of suspicious communications.
Computer Vision for Email Attachments
Attackers often embed malicious intent within images or screenshots, particularly spoofed login pages, QR codes, and brand logos. Computer vision techniques scan visual elements of email content and attachments to identify brand impersonation, pixel-level alterations, and UI deception.
For example, a fake Microsoft login screen may look legitimate to a human user, but computer vision detects discrepancies in alignment, typography, or favicon use, flagging the email before any interaction occurs. This is especially important for preventing credential theft via mobile devices, where visual scrutiny is reduced.
URL Reputation and Link Analysis
Links embedded in phishing emails often lead to malware-hosting sites or fake login pages. URL analysis tools use global cyber threat intelligence feeds to evaluate the safety and destinations of every hyperlink. They inspect URL redirection chains, use sandboxing to test destinations, and identify obfuscated parameters designed to bypass detection. If it detects discrepancies in any of the concerned parameters, the URL and the email get flagged and quarantined before it receivers can interact with it.
Key indicators include:
Typosquatting
IP-based links
Shortened URLs with hidden destinations
Use of special characters or homoglyphs
If a link points to a low-reputation or suspicious domain, it is automatically flagged or disabled.
Header and Domain Anomaly Detection
The header of an email contains metadata that reveals the sending infrastructure. Phishing emails often have forged headers or manipulated routing paths. AI tools inspect SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) configurations to determine sender authenticity.
If an email claims to be from a legitimate source (like http://paypal.com) but fails SPF validation or originates from a misaligned domain, it’s a red flag. This technique is particularly useful for identifying domain spoofing and supply chain impersonation.
Credential Harvesting Detection
Credential harvesting is a core goal of most phishing campaigns. This detection method focuses on identifying attempts to trick users into entering their login details into fraudulent forms or sign-up pages linked to spoofed domains and websites. AT threat detection systems analyze:
Embedded login prompts
iFrame structures
JavaScript behavior mimicking login UIs
These signatures are compared to known legitimate login templates and patterns. If a phishing email redirects to a fake Office365 or Google Workspace login page, even if the design is pixel-perfect, the AI flags the interaction and prevents submission of credentials.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
User and Entity Behavior Analytics tracks and correlates user activities across systems and communications to spot anomalies that may indicate a successful phishing compromise. It looks at login frequency, device fingerprinting, data access patterns, and even email reply behaviors.
For instance, if a user who typically accesses CRM software once a day suddenly downloads a bulk data archive after clicking a suspicious email, UEBA flags it for incident response. It’s particularly useful for detecting lateral movement or privilege escalation after phishing success.
Brand Impersonation Detection
Brand impersonation detection focuses on identifying emails and conversations that mimic well-known corporate brands such as banks, SaaS platforms, cloud providers, and payment gateways to build trust and deceive recipients. This technique uses machine learning and visual comparison tools to match sender branding elements (logos, colors, domain names, footers) with legitimate brand profiles.
For instance, a phishing email might use a cloned PayPal logo and nearly identical visual formatting. Phishing detection tools using machine learning and AI modules compare these design elements to verified brand assets and flag subtle mismatches in resolution, font style, or layout, preventing users from falling for lookalike phishing sites or documents.
Threat Feed Correlation and IOC Matching
This technique leverages global and proprietary threat intelligence feeds to continuously update Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), such as malicious domains, IPs, file hashes, and phishing kit signatures. By correlating incoming email attributes against up-to-date IOC databases, suspicious messages can be rapidly quarantined or rejected before reaching the inbox.
For example, if a URL within an email matches a domain recently associated with phishing campaigns on another network, the system blocks the email instantly. This real-time intelligence sharing is critical for early detection of emerging threats and large-scale phishing waves.
Linguistic Fingerprinting and Stylometry
Linguistic fingerprinting involves profiling the writing style and sentence structure of regular internal and external senders. AI systems develop a “linguistic signature” for each sender based on tone, grammar, vocabulary, and syntax. If an email suddenly deviates from the expected style, such as an HR representative writing in overly formal language or using unfamiliar idioms, it may indicate impersonation or account compromise.
This method is especially effective for stopping internal phishing attempts where attackers gain control of a legitimate email account and try to blend in with organizational communication patterns.
Leverage RiskProfiler to Prevent Phishing Email Attacks
RiskProfiler uses proprietary brand and phishing intelligence modules to identify impersonation attempts and phishing scams. Its phishing detection techniques using machine learning and AI modules tackle these threats head-on with AI-powered analysis, real-time phishing intelligence, and deep visibility across the digital landscape. Here’s how it protects your organization from phishing and impersonation.
AI-Powered Email Security Solutions
RiskProfiler’s AI engine scrutinizes every inbound email within milliseconds, leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) and behavioral profiling to identify anomalies. It detects manipulative language, unusual sender behaviors, and deviations from established communication patterns, effectively flagging potential phishing attempts before they reach the inbox. The platform also maintains historical email breach data, allowing fast detection and flagging of suspicious signatures and phishing attempts.
Visual Brand Impersonation Detection
Leveraging advanced AI-powered image analysis modules, RiskProfiler identifies spoofed logos, counterfeit login screens, and other visual elements commonly used by attackers in phishing attacks. By comparing email visuals against a database of legitimate brand assets, it ensures that deceptive imagery doesn’t mislead recipients. Once flagged, our system notifies your security teams of the threat in real-time, preventing threat escalation.
Attachment Behavior Sandboxing
Suspicious email attachments are executed in a secure, cloud-based sandbox environment. This process analyzes the behavior of attachments in real-time, detecting malware payloads, ransomware, or other malicious activities without risking the organization’s infrastructure.
Advanced Phishing Threat Intelligence Integration
RiskProfiler integrates with global, OSINT, and proprietary threat intelligence feeds, continuously updating its phishing signatures. This real-time email threat intelligence system enables the module to recognize and respond to emerging phishing campaigns, zero-day phishing threats, and other evolving threats promptly. The early awareness and detection help you keep your employees updated and security teams prepared with instantaneous threat data to fend off phishing attempts
Seamless SIEM & Email Gateway Integration
Designed for compatibility, RiskProfiler’s brand and phishing intelligence tool seamlessly integrates with existing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and email gateways. This integration enriches alerts with real-time, contextual data and automates remediation processes, streamlining the organization’s incident response.
Real-Time Alerting & Response
Upon detecting high-risk emails, RiskProfiler instantly quarantines the threats and notifies users with awareness prompts. This immediate action enables security teams to act faster, deploy anti-phishing protocols on time, and reinforce security awareness training among employees for effective protection against email phishing attacks.
Enhanced Protection Through Specialized Phishing Detection Modules
Beyond its core functionalities, RiskProfiler offers specialized modules to address specific aspects of phishing and impersonation threats. These modules does not only secure your internal operations against phishing threats, but also help you maintain your brand image in the target market.
Brand Intelligence & Monitoring
RiskProfiler’s brand intelligence tool proactively monitors the surface web, social media platforms, deep web, and dark web for unauthorized use of brand assets, including logos and trademarks. Using its proprietary advanced AI/ML modules, it detects phishing pages, fake apps, and counterfeit domains, deploys contextual threat reports, enabling fast and informed action for effective contingency and mitigation efforts. It helps you detect phishing campaigns using your brand identity to trick unsuspecting people into giving up their PII details or login credentials. Proactive detection of such phishing campaigns not only helps you protect your clients and customers but also helps you secure your brand identity from being associated with such damaging activities.
Deep and Dark Web Monitoring
RiskProfiler’s dark web monitoring tools continuously scan dark web forums, marketplaces, and chatrooms for leaked credentials, compromised data, and discussions related to potential phishing campaigns. The fast detection allows organizations to flag previously leaked credentials, allowing them to initiate prompt actions like changing login credentials, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), and other secure access management practices for elevated security.
Executive Monitoring
RiskProfiler helps you secure your C-suite executives and key leadership against whaling attacks and spear phishing using its executive intelligence solutions. The platform scans the surface web, online tools, forums, and dark web spaces to analyze and detect malicious conversations targeting your executives. It also uses advanced phishing detection techniques to identify emails and messages trying to manipulate your executives into interacting with malicious content, performing financial transactions, or providing login credentials to suspicious login pages.
Additionally, it detects phishing scams that mimic your executive’s identity or communication patterns to target your employees, clients, or target audience in credential phishing attacks and help you quarantine messages before they can lead to catastrophic cyber threats.
Domain Takedown Services
RiskProfiler continuously surveys the surface and dark web employing automated detection and strategic partnerships to identify and dismantle malicious domains, typosquatted sites, and counterfeit subdomains trying to use your brand identity in phishing scams to target unsuspecting audiences or clients. Leveraging the RiskProfiler brand monitoring and domain take-down solution not only helps you protect your clients from phishing attacks, but it also helps you protect your brand credibility and trust signature in the market.
Phishing is no longer a guessing game—it’s engineered deception. At RiskProfiler, we fight deception with intelligence.
— Setu Parimi, CTO, RiskProfiler
Conclusion
As phishing email attacks continue to evolve, leveraging AI, advanced technological tools, brand impersonation, and social engineering practices, traditional defenses are no longer sufficient. Organizations need a proactive, intelligent approach that not only detects phishing attempts but neutralizes them before they cause harm.
RiskProfiler delivers this with precision. By combining behavioral analytics, NLP, visual recognition, and real-time phishing intelligence, it offers a holistic shield against email-based threats and impersonation campaigns. Whether it’s stopping a spear phishing attempt, detecting spoofed domains, or dismantling fake login pages, RiskProfiler helps you stay one step ahead of attackers with expert phishing detection techniques and streamlined mitigation workflows, while preserving your brand’s integrity and your team’s trust.
Looking for a secure solution to safeguard your business against email phishing attacks?
Book a demo, now!
Email phishing attacks and social engineering are among the most common cybercrimes across the world. However, in recent years, phishing scams have evolved from spammy emails to sophisticated, targeted campaigns. Such highly personalized scamming trends impersonate trusted brands or notable executives, exploit behavioral psychology, and bypass legacy security systems using modern technology. The use of duplicated creatives, brand voice, logos, and other trust symbols makes it quite difficult to distinguish the fakes from the real brand materials, even for the most attentive and tech-savvy people. Additionally, the use of AI technology to mimic a brand’s signatures can enhance the visual accuracy catastrophically, making it difficult to identify the difference without sophisticated phishing detection techniques.
In 2025, when most organizations rely on email sign-ups for lead generation and marketing purposes, email phishing attacks will become one of the leading causes of data breaches, ransomware infections, and financial fraud. With AI-powered phishing intelligence, deepfake voice messages, and real-time domain spoofing, cybercriminals are scaling their attacks faster than ever. Thus, it is imperative for businesses to install effective phishing detection techniques to identify and prevent phishing scams from stealing sensitive organizational data or executing malware attacks.
What Are Phishing Email Attacks?
Phishing means a form of social engineering attack where attackers impersonate legitimate entities, such as banks, SaaS platforms, or trusted executives, to trick recipients into revealing sensitive data, downloading malware, or executing financial transactions. Delivered primarily via email or text messages, phishing scams are often the first step in more complex cyberattacks.

According to the 2021 Cyber Security Threat Trends study conducted by Cisco, 86% of organizations encountered a phishing attack, while the ransomware and malware attack attempts are at 50% and 48%, respectively. A majority of these phishing scams are directly linked to ransomware launches, taking down operations, causing data leaks, financial losses, and considerable damage to organizational trust and reputation.
So, how do employees fall prey to such social engineering attacks? The answer is simple, with careful manipulation.
The content of email phishing attacks uses manipulative language, preying on the receiver’s urgency, trust, and fear in various degrees. Attackers can also imitate trusted executives, advisors, or employees to gain access to sensitive PII details, accelerate app permissions, and complete financial transactions. In the absence of proper phishing detection techniques, organizations can easily fall victim to such fraudulent practices.
Different Types of Phishing Email Attacks
Scammers and cyber attackers use diverse, deceiving methodologies to execute email phishing attacks. With modern cyber threat techniques, criminals now deploy unique phishing plans, each tailored to specific victim identities, platforms, and attack goals using modern technical innovations or AI-assistance. Recognizing these email attack types and their intent is critical for building a robust defense strategy and educating employees on how each variant operates.
In this section, we will be discussing the most common phishing attacks, their targets, and attack intent in detail.

Spear Phishing Attacks
Cyber attackers use Spear Phishing tactics to target specific individuals or departments using personalized information gathered from public sources or prior breaches. These emails often reference internal systems, colleagues, or current projects to build credibility. Thus, these malicious entities often utilize previously stolen information like PII details or sensitive business data from dark web data dumps to carry out attacks on their targets and establish a sense of trust. Since the messages feel relevant and familiar, recipients are more likely to click on malicious links or share credentials, making spear phishing one of the most dangerous forms of email-based attacks.
Whaling Attacks
Whaling attack is a spear phishing campaign where cybercriminals focus specifically on high-level executives such as CEOs, CFOs, or board members. These attacks typically use high-stakes scenarios, like legal threats or urgent financial decisions, to manipulate their targets into seeking immediate action. Because executives often have greater access privileges and weaker scrutiny on their communications, whaling attacks can lead to significant financial losses or reputational damage.
Clone Phishing Attacks
Attackers can, at times, duplicate a legitimate email or text previously received by the target from a trusted contact or known vendor in an attempt to gain the receiver’s trust and influence them to take action. The cloned versions of such emails include identical formatting but swap out the original attachment or link with a malicious one. Victims are easily tricked since the message appears familiar and trustworthy, making this a stealthy and highly effective technique.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC or cyber attacks using Business Email Compromise manipulate email communications between employees, partners, or executives to execute unauthorized actions, such as wire transfers or sensitive data sharing. Attackers may compromise real accounts or create lookalike domains to impersonate internal personnel. BEC attacks are often devoid of malware, making them harder to detect using traditional security filters and requiring behavioral analysis for identification.
Pharming Attacks
Pharming redirects users to fraudulent websites and login pages, even when the correct URL is entered, by exploiting DNS vulnerabilities or infecting a user’s device. These fake sites often mimic login pages of financial institutions, email providers, CRM tools, or internal portals to steal credentials. Unlike phishing emails, pharming doesn’t always require direct user interaction, making it particularly insidious and hard to detect.
Smishing & Vishing Attacks
Smishing (SMS phishing) and vishing (voice phishing) extend phishing tactics beyond email. In smishing, attackers use text messages to deliver malicious links or request sensitive information. Vishing involves fraudulent phone calls, often impersonating customer support or financial institutions. These tactics exploit urgency and trust, and are commonly used in multi-channel phishing campaigns targeting mobile users or remote employees.
Why Is Phishing Detection Using Machine Learning & AI Critical in 2025?
Traditional email security methods such as static blacklists, rule-based filtering, and signature matching were once effective against basic spam and malware. But in 2025, when phishing attacks have become polymorphic, highly targeted, and increasingly evasive, the legacy phishing and manipulation detection systems will not be as useful in detecting particularly advanced phishing emails. Attackers now use advanced tools and AI technologies to craft realistic language, spoof sender identities, and even mimic organizational identity and behavior.
Thus, enabling phishing detection using machine learning can analyze communication patterns, interpret email context, and identify threat signals that humans or legacy tools would miss. Implementation of AI threat detection is not only for risk identification. These advanced modules learns to recognize user behavior and familiar patterns in real-time and adapt with them, to quickly flag anomalies with the most subtle deviation from their usual paths.
Contextual Awareness
AI Large Language Models are trained on billions of messages and are capable of recognizing behavioral patterns from text. Thus, these models are capable of not only interpreting the content but also the intent behind an email. They assess tone, urgency, sentence structure, and historical communication patterns for a detailed contextual analysis. On detection of any suspicious or unusual activity, the system flags it and shuts down the communication.
For example, if an employee suddenly receives an email from a “CEO” demanding an urgent wire transfer, AI can flag the anomaly even if the language appears polished and error-free.
Protection from Zero-Day Phishing Attacks
Zero-day phishing threats are a type of phishing risk where attackers exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems without any prior knowledge. Often in cases of zero-day phishing attacks, attackers target a large number of individuals from the same company to execute their campaign. These scamming techniques can, at times, bypass static filters because they use novel domains, fresh language, and unlisted URLs.
Although these kinds of targeted campaigns can be missed during manual checks, AI modules identify the attack strains easily. AI doesn’t rely on previously known indicators of compromise to recognize a pattern. Instead, it evaluates the behavior, structure, and metadata of each message in real time, flagging suspicious activity even if it’s the first of its kind.
Adaptive Learning
AI systems are trained to learn from new data and evolve with it continuously. As phishing campaigns continue to grow in numbers and diverse attack techniques, the model’s understanding of these tactics keeps evolving with it. This adaptability allows for the detection of newly emerged phishing strains, especially those using advanced obfuscation techniques, visual deception, or multi-stage payload delivery. With AI growing to recognize the attack patterns, the detection and neutralization process grows more favorable for the security teams.
Anomaly Detection with Behavioral Analytics
Enhancing phishing detection using machine learning and AI modules can build a behavioral baseline for each user. This is built based on communication patterns, email sending hours, typical time zones, who they interact with, and their IP signatures. When the machine detects any deviation from this norm, such as an unexpected login location or off-hour message requesting financial action, the system generates high-fidelity alerts without manual input.
Real-Time Decision Making
Speed is of utmost importance when it comes to phishing defense. AI-powered threat detection systems can analyze and score an email’s risk within milliseconds. Followed by this detection, the modules instantly quarantine or flag the dangerous content, blocking all forms of interactions with the contents of the malicious phishing emails. This prevents the user from even viewing the phishing message, reducing response time and minimizing risk exposure.
Streamlined Threat Response
AI-ML modules do not stop at simply detecting phishing threats, they also enable faster, more efficient responses. Once a phishing email is flagged, AI-driven systems can automatically quarantine the message, notify affected users, update threat intelligence feeds, and trigger predefined incident response workflows. This automation dramatically reduces response times and eliminates the bottlenecks of manual triage, allowing security teams to focus on strategic remediation rather than routine firefighting.
Real-World Examples of Phishing Email Attacks
Understanding phishing attacks on companies and their real-world consequences helps illustrate just how conniving and damaging these social engineering attacks can be. Below are some notable phishing attack examples from recent years that highlight evolving attacker tactics and the real consequences of failing to detect them.
Microsoft 365 BEC Campaign (2024)
In 2024, a massive Business Email Compromise (BEC) campaign exploited lookalike domains and impersonated Microsoft 365 support. The attackers sent highly convincing fake invoice emails to finance departments and key personnel across the globe using spear-phishing and adversary-in-the-middle procedures (AiTM). By mimicking internal workflows and targeting shared inboxes, they successfully harvested credentials from over 10,000 companies. Once inside, they initiated unauthorized payments and exfiltrated sensitive financial data, causing millions in aggregate losses.
Crypto Exchange Executive Deepfake (2022)
One of the most startling phishing attacks involved a deepfake video call used to impersonate Binance, the reputed cryptocurrency exchange’s Chief Strategy Officer, Patrick Hillmann. The attackers, using AI-generated visuals and voice synthesis, convinced several crypto community members to interact with the entities regarding asset listing on the crypto exchange platform. The video appeared so realistic that no red flags were raised during the conversation. This incident marked a chilling shift in phishing tactics, where real-time AI impersonation replaced traditional fake emails and documents.
Healthcare Ransomware Phishing Attack (2020)
A phishing campaign disguised as a series of urgent COVID-19 policy updates infiltrated several major US hospitals. The spear phishing emails originated from one of the business executives of Haier Biomedical. In another incident, NCSC detected phishing incidents deploying the “Agent Tesla” malware into a hospital system by disguising itself as Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the Director-General of WHO. Entire hospital systems faced outages, with patient records, lab scheduling, and billing operations affected. Emergency response teams were forced to revert to manual processes, causing dangerous delays in patient care and costing millions in recovery efforts.
Gamma Platform Exploited for Microsoft Credential Theft
Cybercriminals abused the newly launched AI-powered Gamma presentation platform to host phishing pages mimicking Microsoft SharePoint logins, leading to unauthorized access to corporate accounts. In this phishing campaign, attackers use previously compromised email accounts to share phishing emails with users, requesting them to open the embedded PDF document. Opening this PDF leads to a phishing site mimicking Microsoft’s login page with CAPTCHA verification, establishing a false sense of trust with the interacting user.
Top 10 AI Phishing Detection Techniques in 2025
Phishing intelligence is a crucial component of the security protocols in today’s date, given the steep rise in phishing scams. The modern phishing scams are advanced with diligent obscuring techniques, which require AI phishing detection techniques integration for fast identification and takedown. Some of the phishing detection techniques that help you secure your organization and employees from impersonation are listed below.

Behavioral Email Analysis
Behavioral analysis for email threats is one of the most effective phishing detection techniques, where AI modules monitor patterns in sender behavior. The key components of such email security solutions and related analysis include tracking important metadata such as IP addresses, login geographies, and sending times to flag anomalies. The detected and analyzed data is then compared to common business patterns related to trusted senders to flag anomalies.
For example, if a trusted vendor who normally sends invoices from a U.S.-based server suddenly sends an email at 3:00 AM from an Eastern European IP, the system flags it for immediate review. This technique excels at detecting insider threats and compromised accounts.
Natural Language Processing or NLP Phishing Detection
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables email security tools to read and interpret the tone, sentiment, and linguistic structure of messages. Phishing emails often use manipulative language such as urgency, fear, or pressure tactics to influence recipients into taking faster actions.
NLP phishing detection modules evaluate these cues and cross-reference them against known phishing patterns. More advanced models also detect contextual oddities. Such patterns include a supplier suddenly requesting login credentials or an unfamiliar tone from a colleague. This allows for near real-time threat scoring of suspicious communications.
Computer Vision for Email Attachments
Attackers often embed malicious intent within images or screenshots, particularly spoofed login pages, QR codes, and brand logos. Computer vision techniques scan visual elements of email content and attachments to identify brand impersonation, pixel-level alterations, and UI deception.
For example, a fake Microsoft login screen may look legitimate to a human user, but computer vision detects discrepancies in alignment, typography, or favicon use, flagging the email before any interaction occurs. This is especially important for preventing credential theft via mobile devices, where visual scrutiny is reduced.
URL Reputation and Link Analysis
Links embedded in phishing emails often lead to malware-hosting sites or fake login pages. URL analysis tools use global cyber threat intelligence feeds to evaluate the safety and destinations of every hyperlink. They inspect URL redirection chains, use sandboxing to test destinations, and identify obfuscated parameters designed to bypass detection. If it detects discrepancies in any of the concerned parameters, the URL and the email get flagged and quarantined before it receivers can interact with it.
Key indicators include:
Typosquatting
IP-based links
Shortened URLs with hidden destinations
Use of special characters or homoglyphs
If a link points to a low-reputation or suspicious domain, it is automatically flagged or disabled.
Header and Domain Anomaly Detection
The header of an email contains metadata that reveals the sending infrastructure. Phishing emails often have forged headers or manipulated routing paths. AI tools inspect SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) configurations to determine sender authenticity.
If an email claims to be from a legitimate source (like http://paypal.com) but fails SPF validation or originates from a misaligned domain, it’s a red flag. This technique is particularly useful for identifying domain spoofing and supply chain impersonation.
Credential Harvesting Detection
Credential harvesting is a core goal of most phishing campaigns. This detection method focuses on identifying attempts to trick users into entering their login details into fraudulent forms or sign-up pages linked to spoofed domains and websites. AT threat detection systems analyze:
Embedded login prompts
iFrame structures
JavaScript behavior mimicking login UIs
These signatures are compared to known legitimate login templates and patterns. If a phishing email redirects to a fake Office365 or Google Workspace login page, even if the design is pixel-perfect, the AI flags the interaction and prevents submission of credentials.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
User and Entity Behavior Analytics tracks and correlates user activities across systems and communications to spot anomalies that may indicate a successful phishing compromise. It looks at login frequency, device fingerprinting, data access patterns, and even email reply behaviors.
For instance, if a user who typically accesses CRM software once a day suddenly downloads a bulk data archive after clicking a suspicious email, UEBA flags it for incident response. It’s particularly useful for detecting lateral movement or privilege escalation after phishing success.
Brand Impersonation Detection
Brand impersonation detection focuses on identifying emails and conversations that mimic well-known corporate brands such as banks, SaaS platforms, cloud providers, and payment gateways to build trust and deceive recipients. This technique uses machine learning and visual comparison tools to match sender branding elements (logos, colors, domain names, footers) with legitimate brand profiles.
For instance, a phishing email might use a cloned PayPal logo and nearly identical visual formatting. Phishing detection tools using machine learning and AI modules compare these design elements to verified brand assets and flag subtle mismatches in resolution, font style, or layout, preventing users from falling for lookalike phishing sites or documents.
Threat Feed Correlation and IOC Matching
This technique leverages global and proprietary threat intelligence feeds to continuously update Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), such as malicious domains, IPs, file hashes, and phishing kit signatures. By correlating incoming email attributes against up-to-date IOC databases, suspicious messages can be rapidly quarantined or rejected before reaching the inbox.
For example, if a URL within an email matches a domain recently associated with phishing campaigns on another network, the system blocks the email instantly. This real-time intelligence sharing is critical for early detection of emerging threats and large-scale phishing waves.
Linguistic Fingerprinting and Stylometry
Linguistic fingerprinting involves profiling the writing style and sentence structure of regular internal and external senders. AI systems develop a “linguistic signature” for each sender based on tone, grammar, vocabulary, and syntax. If an email suddenly deviates from the expected style, such as an HR representative writing in overly formal language or using unfamiliar idioms, it may indicate impersonation or account compromise.
This method is especially effective for stopping internal phishing attempts where attackers gain control of a legitimate email account and try to blend in with organizational communication patterns.
Leverage RiskProfiler to Prevent Phishing Email Attacks
RiskProfiler uses proprietary brand and phishing intelligence modules to identify impersonation attempts and phishing scams. Its phishing detection techniques using machine learning and AI modules tackle these threats head-on with AI-powered analysis, real-time phishing intelligence, and deep visibility across the digital landscape. Here’s how it protects your organization from phishing and impersonation.
AI-Powered Email Security Solutions
RiskProfiler’s AI engine scrutinizes every inbound email within milliseconds, leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) and behavioral profiling to identify anomalies. It detects manipulative language, unusual sender behaviors, and deviations from established communication patterns, effectively flagging potential phishing attempts before they reach the inbox. The platform also maintains historical email breach data, allowing fast detection and flagging of suspicious signatures and phishing attempts.
Visual Brand Impersonation Detection
Leveraging advanced AI-powered image analysis modules, RiskProfiler identifies spoofed logos, counterfeit login screens, and other visual elements commonly used by attackers in phishing attacks. By comparing email visuals against a database of legitimate brand assets, it ensures that deceptive imagery doesn’t mislead recipients. Once flagged, our system notifies your security teams of the threat in real-time, preventing threat escalation.
Attachment Behavior Sandboxing
Suspicious email attachments are executed in a secure, cloud-based sandbox environment. This process analyzes the behavior of attachments in real-time, detecting malware payloads, ransomware, or other malicious activities without risking the organization’s infrastructure.
Advanced Phishing Threat Intelligence Integration
RiskProfiler integrates with global, OSINT, and proprietary threat intelligence feeds, continuously updating its phishing signatures. This real-time email threat intelligence system enables the module to recognize and respond to emerging phishing campaigns, zero-day phishing threats, and other evolving threats promptly. The early awareness and detection help you keep your employees updated and security teams prepared with instantaneous threat data to fend off phishing attempts
Seamless SIEM & Email Gateway Integration
Designed for compatibility, RiskProfiler’s brand and phishing intelligence tool seamlessly integrates with existing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and email gateways. This integration enriches alerts with real-time, contextual data and automates remediation processes, streamlining the organization’s incident response.
Real-Time Alerting & Response
Upon detecting high-risk emails, RiskProfiler instantly quarantines the threats and notifies users with awareness prompts. This immediate action enables security teams to act faster, deploy anti-phishing protocols on time, and reinforce security awareness training among employees for effective protection against email phishing attacks.
Enhanced Protection Through Specialized Phishing Detection Modules
Beyond its core functionalities, RiskProfiler offers specialized modules to address specific aspects of phishing and impersonation threats. These modules does not only secure your internal operations against phishing threats, but also help you maintain your brand image in the target market.
Brand Intelligence & Monitoring
RiskProfiler’s brand intelligence tool proactively monitors the surface web, social media platforms, deep web, and dark web for unauthorized use of brand assets, including logos and trademarks. Using its proprietary advanced AI/ML modules, it detects phishing pages, fake apps, and counterfeit domains, deploys contextual threat reports, enabling fast and informed action for effective contingency and mitigation efforts. It helps you detect phishing campaigns using your brand identity to trick unsuspecting people into giving up their PII details or login credentials. Proactive detection of such phishing campaigns not only helps you protect your clients and customers but also helps you secure your brand identity from being associated with such damaging activities.
Deep and Dark Web Monitoring
RiskProfiler’s dark web monitoring tools continuously scan dark web forums, marketplaces, and chatrooms for leaked credentials, compromised data, and discussions related to potential phishing campaigns. The fast detection allows organizations to flag previously leaked credentials, allowing them to initiate prompt actions like changing login credentials, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), and other secure access management practices for elevated security.
Executive Monitoring
RiskProfiler helps you secure your C-suite executives and key leadership against whaling attacks and spear phishing using its executive intelligence solutions. The platform scans the surface web, online tools, forums, and dark web spaces to analyze and detect malicious conversations targeting your executives. It also uses advanced phishing detection techniques to identify emails and messages trying to manipulate your executives into interacting with malicious content, performing financial transactions, or providing login credentials to suspicious login pages.
Additionally, it detects phishing scams that mimic your executive’s identity or communication patterns to target your employees, clients, or target audience in credential phishing attacks and help you quarantine messages before they can lead to catastrophic cyber threats.
Domain Takedown Services
RiskProfiler continuously surveys the surface and dark web employing automated detection and strategic partnerships to identify and dismantle malicious domains, typosquatted sites, and counterfeit subdomains trying to use your brand identity in phishing scams to target unsuspecting audiences or clients. Leveraging the RiskProfiler brand monitoring and domain take-down solution not only helps you protect your clients from phishing attacks, but it also helps you protect your brand credibility and trust signature in the market.
Phishing is no longer a guessing game—it’s engineered deception. At RiskProfiler, we fight deception with intelligence.
— Setu Parimi, CTO, RiskProfiler
Conclusion
As phishing email attacks continue to evolve, leveraging AI, advanced technological tools, brand impersonation, and social engineering practices, traditional defenses are no longer sufficient. Organizations need a proactive, intelligent approach that not only detects phishing attempts but neutralizes them before they cause harm.
RiskProfiler delivers this with precision. By combining behavioral analytics, NLP, visual recognition, and real-time phishing intelligence, it offers a holistic shield against email-based threats and impersonation campaigns. Whether it’s stopping a spear phishing attempt, detecting spoofed domains, or dismantling fake login pages, RiskProfiler helps you stay one step ahead of attackers with expert phishing detection techniques and streamlined mitigation workflows, while preserving your brand’s integrity and your team’s trust.
Looking for a secure solution to safeguard your business against email phishing attacks?
Book a demo, now!
Jump to
Share Article
Share Article
Explore Our
Latest Insights
Stay informed with expert perspectives on cybersecurity, attack surface management,
and building digital resilience.
Enterprise-Grade Security & Trust
Specialized intelligence agents working together toprotect your organization
Ready to Transform
Your Threat Management?
Join hundreds of security teams who trust KnyX to cut through the noise and focus on what matters most.
Book a Demo Today

KnyX Agentic AI transforms external threat intelligence into actionable insights, helping security teams focus on what matters most.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
By submitting your email address, you agree to receive RiskProfiler’s monthly newsletter. For more information, please read our privacy policy. You can always withdraw your consent.
Solutions










© 2026 RiskProfiler | All Rights Reserved










© 2026 RiskProfiler | All Rights Reserved










© 2026 RiskProfiler | All Rights Reserved



