Recognized in

®

™ Voice of the Customer 2025 for Brand Protection and External Attack Surface Management


Top Vulnerability Intelligence Strategies in 2025
Top Vulnerability Intelligence Strategies in 2025
As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated, security teams are realizing that individual vulnerabilities are rarely the whole story.
Read Time
7 min read
Posted On
Mar 27, 2025
Social Media
In today’s constantly evolving cyber threat landscape, organizations are under relentless pressure to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. With threat actors evolving their attack techniques and vulnerabilities surfacing daily, staying ahead of exploits requires more than just routine patching—it demands a strategic approach built around real-time vulnerability intelligence and the right vulnerability management tools.
In this blog, we explore the core scanning methods, proven patching strategies, and top tools for vulnerability management. We’ll also dive into how RiskProfiler empowers teams to proactively track and mitigate vulnerabilities with greater accuracy and speed.
What is Vulnerability Intelligence?
Vulnerability intelligence refers to the continuous process of monitoring, identifying, assessing, and contextualizing software and infrastructure weaknesses using actionable data. Unlike basic scanning, which only detects known issues, vulnerability intelligence adds a layer of prioritization based on exploitability, asset context, and real-world threat activity.
Effective vulnerability intelligence helps organizations:
Understand which vulnerabilities are actively exploited in the wild
Prioritize remediation based on business impact and risk
Align security actions with broader threat intelligence
It transforms raw data into strategic decision-making power—making it essential in reducing your attack surface.
Common Vulnerability Scanning Methods
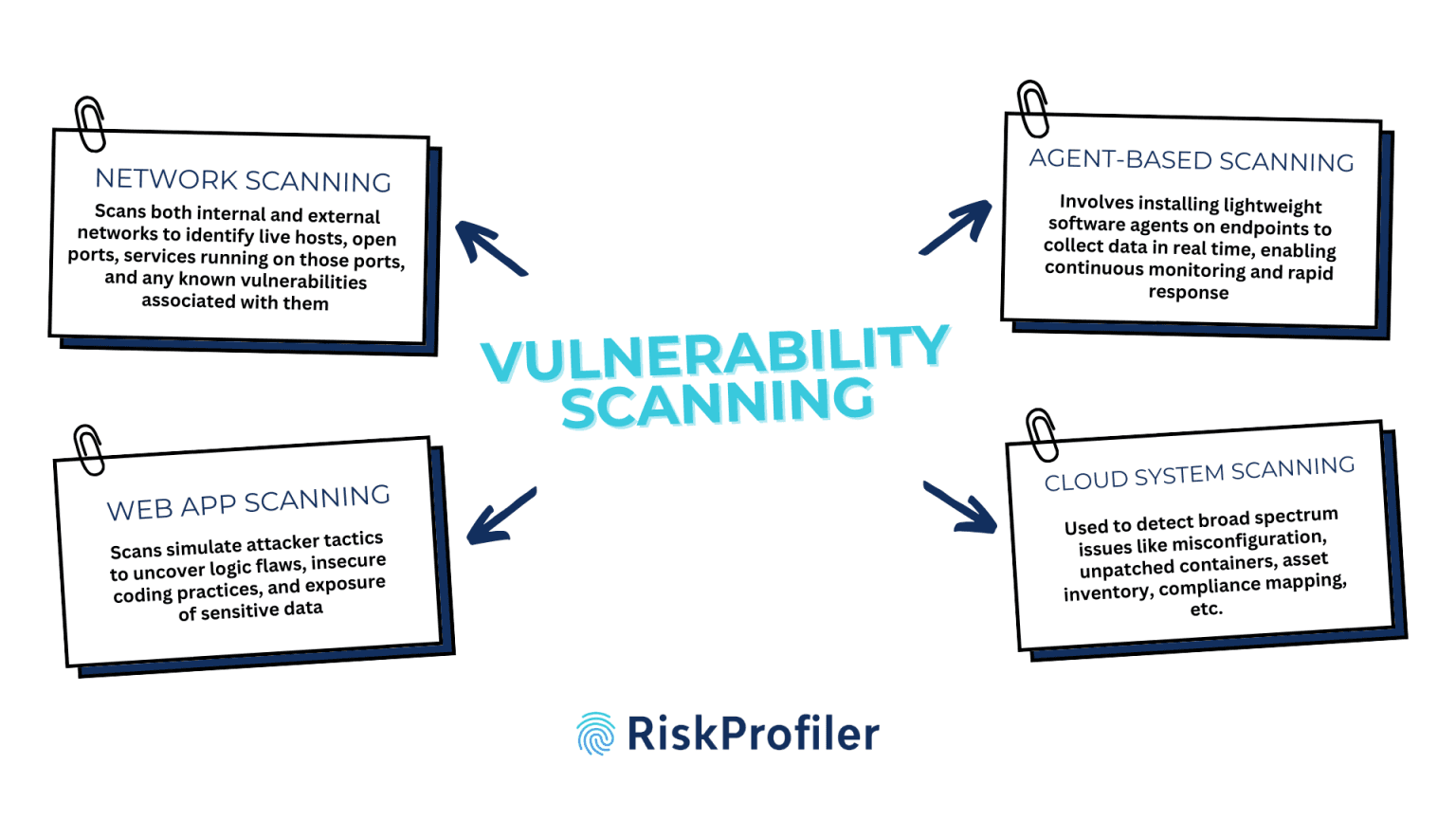
Effective vulnerability management begins with accurate detection. Organizations must leverage a variety of scanning methods to uncover hidden weaknesses across networks, web applications, endpoints, and cloud environments—enabling proactive risk mitigation before attackers can exploit them. Here are the key scanning approaches used today:
1. Network Scanning
Network scanning is the cornerstone of vulnerability management and is often the first step in understanding an organization’s attack surface. This technique involves scanning both internal and external networks to identify live hosts, open ports, services running on those ports, and any known vulnerabilities associated with them.
External Network Scanning focuses on perimeter assets—those exposed to the internet. These scans simulate what a threat actor sees when probing your infrastructure from the outside. Identifying open RDP ports, outdated SSL certificates, or exposed services like FTP can help organizations proactively shut down easy entry points.
Internal Network Scanning is equally vital. It maps assets inside the firewall to detect potential lateral movement paths in the event of a breach. For example, it might uncover vulnerable SMB protocols or misconfigured access control on shared resources.
Best practices include scheduling scans regularly, especially after asset changes, and using authenticated scanning where possible to get deeper insights.
2. Web Application Scanning
Web application scanning targets vulnerabilities within dynamic websites, web apps, and APIs—often among the most targeted parts of an organization’s infrastructure. These scans simulate attacker tactics to uncover logic flaws, insecure coding practices, and exposure of sensitive data.
Tools typically test against the OWASP Top 10, which includes vulnerabilities like SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), and Security Misconfiguration.
Modern scanners also handle JavaScript-heavy single-page applications (SPAs) and dynamic content, which traditional scanners might miss. They often include features like authentication handling, parameter fuzzing, and in-depth DOM inspection.
Beyond traditional vulnerabilities, they check for business logic flaws, such as bypassing payment steps or manipulating discount codes—issues that can have a direct financial impact.
Web scanning is essential for organizations with customer-facing portals, mobile backends, or partner-integrated APIs.
3. Agent-Based Scanning
Agent-based scanning involves installing lightweight software agents on endpoints (workstations, servers, containers) to monitor vulnerabilities from the inside out. These agents collect data in real time, enabling continuous monitoring and rapid response.
Unlike network scans that rely on what’s externally observable, agents provide granular visibility into installed applications, OS configurations, patch levels, and user behavior.
They are especially effective in remote work environments or highly dynamic infrastructure like virtual machines or Kubernetes clusters, where traditional scanning may miss short-lived assets.
Many agents support real-time alerting and can trigger patch deployment automation based on vulnerability severity and risk score.
Challenges include initial deployment, resource consumption, and managing agent health across a distributed network—but the tradeoff is richer, more actionable insights.
4. Cloud Environment Scanning
As companies continue to switch to cloud service providers such as AWS, Azure, and GCP for managing operational efficiency and improving accessibility and scalability, cloud environment scanning has become a vital component of modern vulnerability management.
These scans detect a broad spectrum of issues:
Misconfigurations such as publicly accessible S3 buckets, overly permissive IAM roles, and open databases.
Unpatched containers and vulnerable images running in orchestration platforms like Kubernetes.
Drift from baseline configurations and lack of encryption at rest or in transit.
Cloud-native scanning tools integrate with APIs from cloud providers to gain continuous visibility into changing asset inventories, ensuring newly provisioned resources don’t introduce risk.
Combining scanning with Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) enhances this capability by adding governance, compliance mapping (e.g., to CIS benchmarks), and real-time alerting.
Given the ephemeral nature of cloud assets, traditional scanning methods may fall short—cloud environment scanning ensures you’re not blind to risks in serverless functions, containers, and auto-scaling environments.
Patch Management Best Practices
Patch management is a critical component of vulnerability management that, when executed correctly, can drastically reduce the window of exposure to known threats. However, with thousands of vulnerabilities discovered each year, organizations need a well-structured path management strategy to maintain order and effectiveness.
Below are four best practices to ensure your patch management process is both efficient and effective:
1. Risk-Based Prioritization
In today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, not all vulnerabilities are created equal. Treating every security flaw with the same level of urgency leads to inefficient resource allocation and increases the risk of missing critical issues. This is where risk-based vulnerability prioritization becomes essential.
Beyond CVSS: Understanding the True Risk
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides a helpful baseline for understanding the severity of a vulnerability, but it doesn’t offer the full picture. CVSS scores are static and often fail to account for real-world exploitability, business impact, and contextual relevance.
To effectively prioritize vulnerabilities, organizations must go beyond CVSS and incorporate additional layers of intelligence, including:
Exploitability Data
Is the vulnerability actively being exploited in the wild? Real-time threat intelligence feeds that monitor exploit activity can help security teams understand which weaknesses are being targeted by attackers and require immediate attention.
Asset Criticality
How important is the affected system to your business operations? A vulnerability on a high-value asset—like a financial server or customer-facing application—carries greater risk than one on a low-impact system. Prioritize based on business function and impact.
Exposure Status
Is the vulnerable asset exposed to the internet or contained within internal infrastructure? Internet-facing assets present a higher attack surface and are more likely to be targeted by opportunistic or automated attacks.
Leverage Contextual Vulnerability Intelligence
Modern vulnerability intelligence platforms combine these data points into a unified risk score, offering real-time, actionable context. By integrating threat intelligence, asset context, and exploitability data, these platforms empower security teams to make faster, more informed decisions—reducing response time and improving operational efficiency.
Reduce Risk, Not Just Vulnerabilities
Adopting a risk-based approach ensures that the most dangerous vulnerabilities are addressed first, reducing the likelihood of a successful cyberattack. This method helps organizations stay ahead of opportunistic and targeted threats while optimizing team efforts and resources.
2. Automated Patch Deployment
Manual patching is time-consuming, error-prone, and inefficient at scale. Automation not only accelerates the remediation process but also ensures consistency across the enterprise.
Use patch management tools that integrate with your asset inventory and vulnerability scanners to automate patch distribution based on priority.
Implement policies for automated patching of low-risk systems while reserving manual intervention for sensitive assets.
Ensure rollback capabilities are built into your automation processes, allowing teams to quickly revert patches that cause system instability or compatibility issues.
Automation doesn’t eliminate the need for oversight—but it does empower your team to handle patching with speed and precision.
3. Staging and Testing
Before rolling out patches across production systems, it’s crucial to stage and test them in a controlled environment.
Establish a staging environment that closely mirrors your production infrastructure.
Run validation tests to ensure patches don’t conflict with existing software or configurations.
Pay special attention to custom applications, legacy systems, and third-party integrations, which are more prone to issues post-patching.
This extra step minimizes the risk of downtime or performance degradation—protecting both security and operational continuity.
4. Regular Patch Audits
A successful patch management program isn’t just about deploying fixes—it’s about verifying that remediation has actually occurred.
Conduct regular audits to assess:
Which systems are fully patched
Which are pending or failed
Any systems that were excluded (intentionally or unintentionally)
Document exceptions and rationale (e.g., business-critical systems where patches require vendor approval or longer testing cycles).
Use audit findings to fine-tune your patching cadence and improve coordination between IT, security, and operations teams.
Patch audits also help demonstrate compliance with security frameworks and regulations like ISO 27001, NIST, and PCI DSS.
How RiskProfiler Enhances Vulnerability Intelligence?
In today’s rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape, organizations require advanced tools to manage vulnerabilities effectively and safeguard critical assets. RiskProfiler stands out by offering a comprehensive vulnerability management solution that transcends traditional scanning methods, providing deep insights and proactive defense mechanisms. Here’s an in-depth look at how RiskProfiler enhances vulnerability intelligence:
Continuous External Attack Surface Monitoring
RiskProfiler provides real-time visibility into all internet-facing assets, ensuring organizations maintain an up-to-date inventory of their external digital footprint. By continuously monitoring these assets, RiskProfiler identifies potential vulnerabilities and exposures, enabling security teams to address issues before they can be exploited by malicious actors. This proactive external attack surface management approach is crucial for maintaining a robust security posture in an era where external threats are increasingly sophisticated.
Prioritized Vulnerability Alerts
Not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk. RiskProfiler assesses each vulnerability’s severity and potential impact using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), combined with contextual factors such as exploit intelligence, threat actor activity, and asset criticality. This prioritization ensures that security teams can focus their remediation efforts on the most critical threats, optimizing resource allocation and reducing the window of exposure.
Unified Dashboard for Comprehensive Oversight
Managing vulnerabilities across various environments can be complex. RiskProfiler simplifies this by offering a unified dashboard that centralizes information on third-party, internal, and cloud vulnerabilities. This consolidated view facilitates streamlined triage and response processes, allowing security teams to efficiently manage and mitigate risks across the entire organization.
Attack Path Analysis
Understanding how attackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities is key to effective defense. RiskProfiler scans systems, applications, and networks to map out potential attack paths, providing a visual representation of possible exploitation routes. This insight enables organizations to identify and fortify weak points, effectively disrupting potential attack chains before they can be leveraged by adversaries.
Threat Comparison
RiskProfiler allows organizations to compare and evaluate their threat exposure against different entities or industry benchmarks. This comprehensive scoring and visualized data provide valuable context, helping security teams understand their relative security posture and identify areas for improvement.
Automated Remediation Workflows
Timely remediation is critical in vulnerability management. RiskProfiler offers automated workflows that expedite the resolution of identified vulnerabilities, reducing downtime and ensuring systems remain secure. These workflows provide clear, step-by-step solutions that align with operational processes, facilitating seamless and efficient remediation.
Proactive Monitoring and Real-Time Alerts
RiskProfiler’s proactive monitoring capabilities ensure continuous surveillance of systems and attack surfaces. By staying vigilant, the platform can detect new risks as they emerge and provide instant, tailored alerts. This real-time notification system empowers security teams to respond swiftly to emerging threats, maintaining uninterrupted business operations.
Seamless Integrations for Enhanced Efficiency
Integrating new tools into existing security infrastructures can be challenging. RiskProfiler addresses this by offering seamless integrations with cloud platforms, ticketing systems, and other security tools. This ensures cohesive workflows and efficient management of security operations, enhancing the organization’s overall ability to detect and respond to threats.
Strategies to Stay Ahead of Cyber Attacks
While advanced tools provide critical capabilities, their effectiveness hinges on a well-orchestrated strategy. The following key approaches will help elevate your vulnerability management program and ensure resilience against today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape.
1. Adopt a Continuous Management Cycle
Transitioning from periodic vulnerability scans to a continuous management cycle allows for real-time detection, assessment, and remediation. This approach minimizes the window of exposure and ensures vulnerabilities are addressed as soon as they appear, not weeks later.
2. Leverage Threat Intelligence
Enrich vulnerability data with threat intelligence—such as exploit availability, attacker behavior, and active campaigns—to understand which vulnerabilities are actually being weaponized. This context helps security teams prioritize effectively and stay ahead of emerging threats and zero-day exploits.
3. Map Vulnerabilities to Business Risk
Not all vulnerabilities impact your business equally. By aligning technical findings with asset criticality, revenue impact, and compliance requirements, organizations can prioritize remediation efforts that reduce the most business-relevant risk, rather than just focusing on high CVSS scores.
4. Automate Where Possible
Automation helps reduce human error and accelerates response times. From vulnerability scanning to patch deployment and alerting, automating routine tasks allows security teams to focus on strategic initiatives while ensuring consistent and timely remediation of known issues.
5. Red and Blue Team Collaboration
Implementing a red-blue team collaboration strategy can be effective in dealing with hidden system vulnerabilities. Red teams simulate real-world attacks to test defenses, while blue teams work to detect and stop them. Their collaboration fosters a more resilient security posture by identifying blind spots and validating the effectiveness of detection and response processes.
6. Train Your Teams
Security is a shared responsibility. Regularly educate developers, IT, and security staff on evolving threat landscapes, secure coding practices, and vulnerability response procedures. Well-informed teams are faster to react and less likely to introduce risk through misconfigurations or errors.
Final Words,
Staying ahead of cyber threats means going beyond traditional scanning and patching. With the right combination of vulnerability intelligence, proactive strategies, and advanced vulnerability management tools, organizations can dramatically reduce their risk exposure.
RiskProfiler brings clarity, context, and control to vulnerability management—empowering your team to respond faster, smarter, and with greater confidence.
Ready to level up your vulnerability intelligence?
Book a demo or get in touch with the RiskProfiler team today.
In today’s constantly evolving cyber threat landscape, organizations are under relentless pressure to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. With threat actors evolving their attack techniques and vulnerabilities surfacing daily, staying ahead of exploits requires more than just routine patching—it demands a strategic approach built around real-time vulnerability intelligence and the right vulnerability management tools.
In this blog, we explore the core scanning methods, proven patching strategies, and top tools for vulnerability management. We’ll also dive into how RiskProfiler empowers teams to proactively track and mitigate vulnerabilities with greater accuracy and speed.
What is Vulnerability Intelligence?
Vulnerability intelligence refers to the continuous process of monitoring, identifying, assessing, and contextualizing software and infrastructure weaknesses using actionable data. Unlike basic scanning, which only detects known issues, vulnerability intelligence adds a layer of prioritization based on exploitability, asset context, and real-world threat activity.
Effective vulnerability intelligence helps organizations:
Understand which vulnerabilities are actively exploited in the wild
Prioritize remediation based on business impact and risk
Align security actions with broader threat intelligence
It transforms raw data into strategic decision-making power—making it essential in reducing your attack surface.
Common Vulnerability Scanning Methods

Effective vulnerability management begins with accurate detection. Organizations must leverage a variety of scanning methods to uncover hidden weaknesses across networks, web applications, endpoints, and cloud environments—enabling proactive risk mitigation before attackers can exploit them. Here are the key scanning approaches used today:
1. Network Scanning
Network scanning is the cornerstone of vulnerability management and is often the first step in understanding an organization’s attack surface. This technique involves scanning both internal and external networks to identify live hosts, open ports, services running on those ports, and any known vulnerabilities associated with them.
External Network Scanning focuses on perimeter assets—those exposed to the internet. These scans simulate what a threat actor sees when probing your infrastructure from the outside. Identifying open RDP ports, outdated SSL certificates, or exposed services like FTP can help organizations proactively shut down easy entry points.
Internal Network Scanning is equally vital. It maps assets inside the firewall to detect potential lateral movement paths in the event of a breach. For example, it might uncover vulnerable SMB protocols or misconfigured access control on shared resources.
Best practices include scheduling scans regularly, especially after asset changes, and using authenticated scanning where possible to get deeper insights.
2. Web Application Scanning
Web application scanning targets vulnerabilities within dynamic websites, web apps, and APIs—often among the most targeted parts of an organization’s infrastructure. These scans simulate attacker tactics to uncover logic flaws, insecure coding practices, and exposure of sensitive data.
Tools typically test against the OWASP Top 10, which includes vulnerabilities like SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), and Security Misconfiguration.
Modern scanners also handle JavaScript-heavy single-page applications (SPAs) and dynamic content, which traditional scanners might miss. They often include features like authentication handling, parameter fuzzing, and in-depth DOM inspection.
Beyond traditional vulnerabilities, they check for business logic flaws, such as bypassing payment steps or manipulating discount codes—issues that can have a direct financial impact.
Web scanning is essential for organizations with customer-facing portals, mobile backends, or partner-integrated APIs.
3. Agent-Based Scanning
Agent-based scanning involves installing lightweight software agents on endpoints (workstations, servers, containers) to monitor vulnerabilities from the inside out. These agents collect data in real time, enabling continuous monitoring and rapid response.
Unlike network scans that rely on what’s externally observable, agents provide granular visibility into installed applications, OS configurations, patch levels, and user behavior.
They are especially effective in remote work environments or highly dynamic infrastructure like virtual machines or Kubernetes clusters, where traditional scanning may miss short-lived assets.
Many agents support real-time alerting and can trigger patch deployment automation based on vulnerability severity and risk score.
Challenges include initial deployment, resource consumption, and managing agent health across a distributed network—but the tradeoff is richer, more actionable insights.
4. Cloud Environment Scanning
As companies continue to switch to cloud service providers such as AWS, Azure, and GCP for managing operational efficiency and improving accessibility and scalability, cloud environment scanning has become a vital component of modern vulnerability management.
These scans detect a broad spectrum of issues:
Misconfigurations such as publicly accessible S3 buckets, overly permissive IAM roles, and open databases.
Unpatched containers and vulnerable images running in orchestration platforms like Kubernetes.
Drift from baseline configurations and lack of encryption at rest or in transit.
Cloud-native scanning tools integrate with APIs from cloud providers to gain continuous visibility into changing asset inventories, ensuring newly provisioned resources don’t introduce risk.
Combining scanning with Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) enhances this capability by adding governance, compliance mapping (e.g., to CIS benchmarks), and real-time alerting.
Given the ephemeral nature of cloud assets, traditional scanning methods may fall short—cloud environment scanning ensures you’re not blind to risks in serverless functions, containers, and auto-scaling environments.
Patch Management Best Practices
Patch management is a critical component of vulnerability management that, when executed correctly, can drastically reduce the window of exposure to known threats. However, with thousands of vulnerabilities discovered each year, organizations need a well-structured path management strategy to maintain order and effectiveness.
Below are four best practices to ensure your patch management process is both efficient and effective:
1. Risk-Based Prioritization
In today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, not all vulnerabilities are created equal. Treating every security flaw with the same level of urgency leads to inefficient resource allocation and increases the risk of missing critical issues. This is where risk-based vulnerability prioritization becomes essential.
Beyond CVSS: Understanding the True Risk
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides a helpful baseline for understanding the severity of a vulnerability, but it doesn’t offer the full picture. CVSS scores are static and often fail to account for real-world exploitability, business impact, and contextual relevance.
To effectively prioritize vulnerabilities, organizations must go beyond CVSS and incorporate additional layers of intelligence, including:
Exploitability Data
Is the vulnerability actively being exploited in the wild? Real-time threat intelligence feeds that monitor exploit activity can help security teams understand which weaknesses are being targeted by attackers and require immediate attention.
Asset Criticality
How important is the affected system to your business operations? A vulnerability on a high-value asset—like a financial server or customer-facing application—carries greater risk than one on a low-impact system. Prioritize based on business function and impact.
Exposure Status
Is the vulnerable asset exposed to the internet or contained within internal infrastructure? Internet-facing assets present a higher attack surface and are more likely to be targeted by opportunistic or automated attacks.
Leverage Contextual Vulnerability Intelligence
Modern vulnerability intelligence platforms combine these data points into a unified risk score, offering real-time, actionable context. By integrating threat intelligence, asset context, and exploitability data, these platforms empower security teams to make faster, more informed decisions—reducing response time and improving operational efficiency.
Reduce Risk, Not Just Vulnerabilities
Adopting a risk-based approach ensures that the most dangerous vulnerabilities are addressed first, reducing the likelihood of a successful cyberattack. This method helps organizations stay ahead of opportunistic and targeted threats while optimizing team efforts and resources.
2. Automated Patch Deployment
Manual patching is time-consuming, error-prone, and inefficient at scale. Automation not only accelerates the remediation process but also ensures consistency across the enterprise.
Use patch management tools that integrate with your asset inventory and vulnerability scanners to automate patch distribution based on priority.
Implement policies for automated patching of low-risk systems while reserving manual intervention for sensitive assets.
Ensure rollback capabilities are built into your automation processes, allowing teams to quickly revert patches that cause system instability or compatibility issues.
Automation doesn’t eliminate the need for oversight—but it does empower your team to handle patching with speed and precision.
3. Staging and Testing
Before rolling out patches across production systems, it’s crucial to stage and test them in a controlled environment.
Establish a staging environment that closely mirrors your production infrastructure.
Run validation tests to ensure patches don’t conflict with existing software or configurations.
Pay special attention to custom applications, legacy systems, and third-party integrations, which are more prone to issues post-patching.
This extra step minimizes the risk of downtime or performance degradation—protecting both security and operational continuity.
4. Regular Patch Audits
A successful patch management program isn’t just about deploying fixes—it’s about verifying that remediation has actually occurred.
Conduct regular audits to assess:
Which systems are fully patched
Which are pending or failed
Any systems that were excluded (intentionally or unintentionally)
Document exceptions and rationale (e.g., business-critical systems where patches require vendor approval or longer testing cycles).
Use audit findings to fine-tune your patching cadence and improve coordination between IT, security, and operations teams.
Patch audits also help demonstrate compliance with security frameworks and regulations like ISO 27001, NIST, and PCI DSS.
How RiskProfiler Enhances Vulnerability Intelligence?
In today’s rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape, organizations require advanced tools to manage vulnerabilities effectively and safeguard critical assets. RiskProfiler stands out by offering a comprehensive vulnerability management solution that transcends traditional scanning methods, providing deep insights and proactive defense mechanisms. Here’s an in-depth look at how RiskProfiler enhances vulnerability intelligence:
Continuous External Attack Surface Monitoring
RiskProfiler provides real-time visibility into all internet-facing assets, ensuring organizations maintain an up-to-date inventory of their external digital footprint. By continuously monitoring these assets, RiskProfiler identifies potential vulnerabilities and exposures, enabling security teams to address issues before they can be exploited by malicious actors. This proactive external attack surface management approach is crucial for maintaining a robust security posture in an era where external threats are increasingly sophisticated.
Prioritized Vulnerability Alerts
Not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk. RiskProfiler assesses each vulnerability’s severity and potential impact using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), combined with contextual factors such as exploit intelligence, threat actor activity, and asset criticality. This prioritization ensures that security teams can focus their remediation efforts on the most critical threats, optimizing resource allocation and reducing the window of exposure.
Unified Dashboard for Comprehensive Oversight
Managing vulnerabilities across various environments can be complex. RiskProfiler simplifies this by offering a unified dashboard that centralizes information on third-party, internal, and cloud vulnerabilities. This consolidated view facilitates streamlined triage and response processes, allowing security teams to efficiently manage and mitigate risks across the entire organization.
Attack Path Analysis
Understanding how attackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities is key to effective defense. RiskProfiler scans systems, applications, and networks to map out potential attack paths, providing a visual representation of possible exploitation routes. This insight enables organizations to identify and fortify weak points, effectively disrupting potential attack chains before they can be leveraged by adversaries.
Threat Comparison
RiskProfiler allows organizations to compare and evaluate their threat exposure against different entities or industry benchmarks. This comprehensive scoring and visualized data provide valuable context, helping security teams understand their relative security posture and identify areas for improvement.
Automated Remediation Workflows
Timely remediation is critical in vulnerability management. RiskProfiler offers automated workflows that expedite the resolution of identified vulnerabilities, reducing downtime and ensuring systems remain secure. These workflows provide clear, step-by-step solutions that align with operational processes, facilitating seamless and efficient remediation.
Proactive Monitoring and Real-Time Alerts
RiskProfiler’s proactive monitoring capabilities ensure continuous surveillance of systems and attack surfaces. By staying vigilant, the platform can detect new risks as they emerge and provide instant, tailored alerts. This real-time notification system empowers security teams to respond swiftly to emerging threats, maintaining uninterrupted business operations.
Seamless Integrations for Enhanced Efficiency
Integrating new tools into existing security infrastructures can be challenging. RiskProfiler addresses this by offering seamless integrations with cloud platforms, ticketing systems, and other security tools. This ensures cohesive workflows and efficient management of security operations, enhancing the organization’s overall ability to detect and respond to threats.
Strategies to Stay Ahead of Cyber Attacks
While advanced tools provide critical capabilities, their effectiveness hinges on a well-orchestrated strategy. The following key approaches will help elevate your vulnerability management program and ensure resilience against today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape.
1. Adopt a Continuous Management Cycle
Transitioning from periodic vulnerability scans to a continuous management cycle allows for real-time detection, assessment, and remediation. This approach minimizes the window of exposure and ensures vulnerabilities are addressed as soon as they appear, not weeks later.
2. Leverage Threat Intelligence
Enrich vulnerability data with threat intelligence—such as exploit availability, attacker behavior, and active campaigns—to understand which vulnerabilities are actually being weaponized. This context helps security teams prioritize effectively and stay ahead of emerging threats and zero-day exploits.
3. Map Vulnerabilities to Business Risk
Not all vulnerabilities impact your business equally. By aligning technical findings with asset criticality, revenue impact, and compliance requirements, organizations can prioritize remediation efforts that reduce the most business-relevant risk, rather than just focusing on high CVSS scores.
4. Automate Where Possible
Automation helps reduce human error and accelerates response times. From vulnerability scanning to patch deployment and alerting, automating routine tasks allows security teams to focus on strategic initiatives while ensuring consistent and timely remediation of known issues.
5. Red and Blue Team Collaboration
Implementing a red-blue team collaboration strategy can be effective in dealing with hidden system vulnerabilities. Red teams simulate real-world attacks to test defenses, while blue teams work to detect and stop them. Their collaboration fosters a more resilient security posture by identifying blind spots and validating the effectiveness of detection and response processes.
6. Train Your Teams
Security is a shared responsibility. Regularly educate developers, IT, and security staff on evolving threat landscapes, secure coding practices, and vulnerability response procedures. Well-informed teams are faster to react and less likely to introduce risk through misconfigurations or errors.
Final Words,
Staying ahead of cyber threats means going beyond traditional scanning and patching. With the right combination of vulnerability intelligence, proactive strategies, and advanced vulnerability management tools, organizations can dramatically reduce their risk exposure.
RiskProfiler brings clarity, context, and control to vulnerability management—empowering your team to respond faster, smarter, and with greater confidence.
Ready to level up your vulnerability intelligence?
Book a demo or get in touch with the RiskProfiler team today.
Jump to
Share Article
Share Article
Explore Our
Latest Insights
Stay informed with expert perspectives on cybersecurity, attack surface management,
and building digital resilience.
Enterprise-Grade Security & Trust
Specialized intelligence agents working together toprotect your organization
Ready to Transform
Your Threat Management?
Join hundreds of security teams who trust KnyX to cut through the noise and focus on what matters most.
Book a Demo Today

KnyX Agentic AI transforms external threat intelligence into actionable insights, helping security teams focus on what matters most.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
By submitting your email address, you agree to receive RiskProfiler’s monthly newsletter. For more information, please read our privacy policy. You can always withdraw your consent.
Solutions










© 2026 RiskProfiler | All Rights Reserved










© 2026 RiskProfiler | All Rights Reserved










© 2026 RiskProfiler | All Rights Reserved



